Integration tool: pyFAI-integrate¶
Purpose¶
PyFAI-integrate is a graphical interface (based on Python/Qt4) to perform azimuthal integration on a set of files. It exposes most of the important options available within pyFAI and allows you to select a GPU (or an openCL platform) to perform the calculation on.
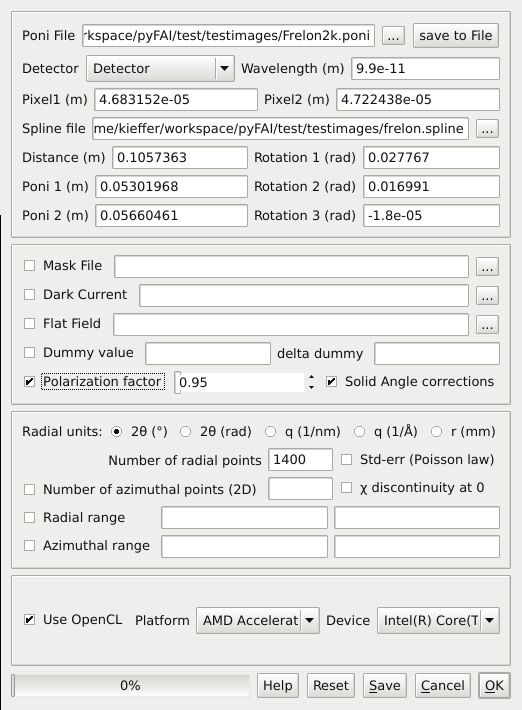
Usage¶
pyFAI-integrate [options] file1.edf file2.edf ...
Options:¶
--version show program’s version number and exit -h, --help show help message and exit -v, --verbose switch to verbose/debug mode -o OUTPUT, --output=OUTPUT Directory or file where to store the output data
Tips & Tricks:¶
PyFAI-integrate saves all parameters in a .azimint.json (hidden) file. This JSON file is an ascii file which can be edited and used to configure online data analysis using the LImA plugin of pyFAI.
Nota: there is bug in debian6 making the GUI crash (to be fixed inside pyqt) http://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi?bug=697348
Example:¶
$ pyFAI-integrate --help
usage: pyFAI-integrate [options] file1.edf file2.edf ...
PyFAI-integrate is a graphical interface (based on Python/Qt4) to perform
azimuthal integration on a set of files. It exposes most of the important
options available within pyFAI and allows you to select a GPU (or an openCL
platform) to perform the calculation on.
positional arguments:
FILE Files to be integrated
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-V, --version show program's version number and exit
-v, --verbose switch to verbose/debug mode
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Directory or file where to store the output data
-f FORMAT, --format FORMAT
output data format (can be HDF5)
-s SLOW, --slow-motor SLOW
Dimension of the scan on the slow direction (makes
sense only with HDF5)
-r RAPID, --fast-motor RAPID
Dimension of the scan on the fast direction (makes
sense only with HDF5)
--no-gui Process the dataset without showing the user
interface.
-j JSON, --json JSON Configuration file containing the processing to be
done
--monitor-name MONITOR_KEY
Name of the monitor in the header of each input files.
If defined the contribution of each input file is
divided by the monitor. If the header does not contain
or contains a wrong value, the contribution of the
input file is ignored. On EDF files, values from
'counter_pos' can accessed by using the expected
mnemonic. For example 'counter/bmon'.
PyFAI-integrate saves all parameters in a .azimint.json (hidden) file. This
JSON file is an ascii file which can be edited and used to configure online
data analysis using the LImA plugin of pyFAI. Nota: there is bug in debian6
making the GUI crash (to be fixed inside pyqt) http://bugs.debian.org/cgi-
bin/bugreport.cgi?bug=697348