Integration tool: diff_map¶
Purpose¶
Azimuthal integration for diffraction imaging
Diffraction mapping is an imaging experiment where 2D diffraction patterns are recorded while performing a 2D scan along two axes, one slower and the other fastest.
Diff_map provides a Graphical User Interface (based on top of PyQt, pyFAI and h5py) which allows the reduction of this 4D dataset into a 3D dataset containing the two dimension of movement and the many diffraction angles (the output can be q-space for PDF-CT).
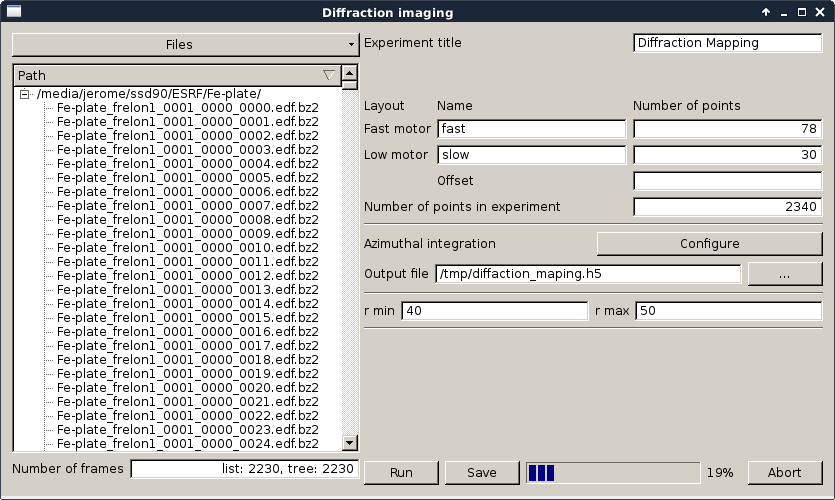
On the left-hand side, the user can select a bunch of files to be processed. For now, any image format supported by FabIO is possible, including multi-frame images, but not ye NeXus files (work ongoing).
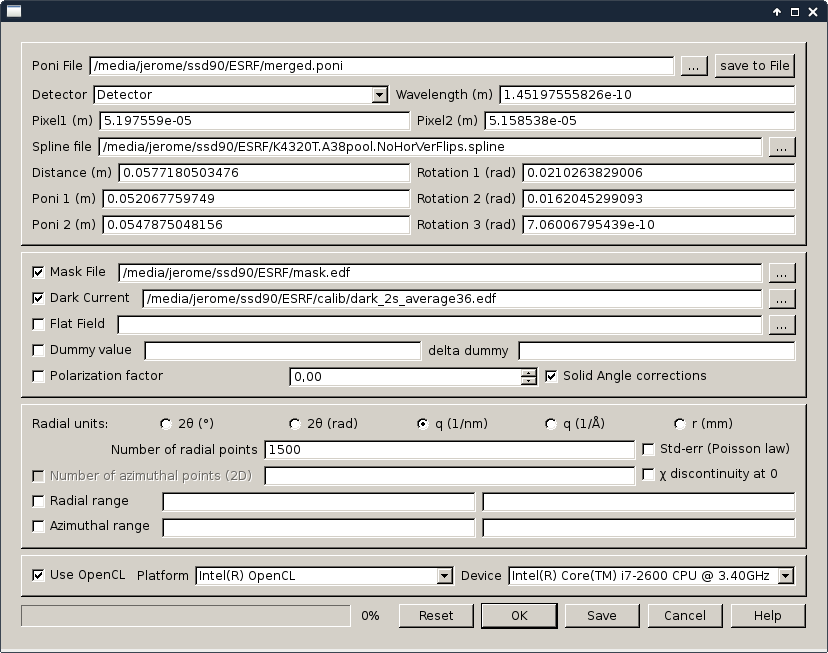
On the right-hand side, the motor range can be specified togeather with their names. The diffraction parameters can be setup in a similar way to pyFAI-integrate. The output name can also be specified.
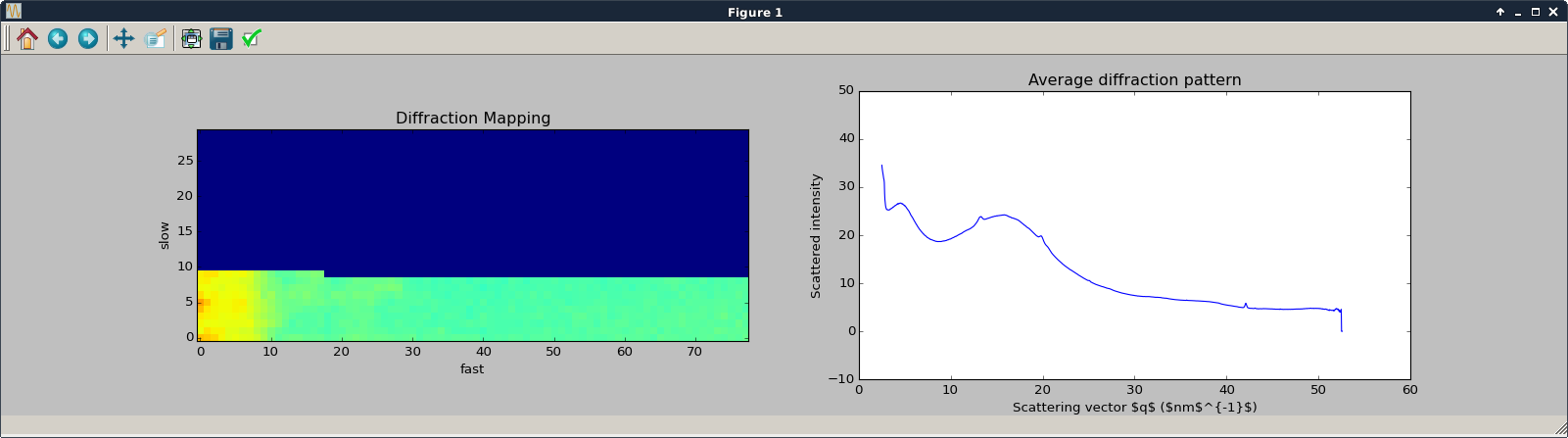
The processing is launched using the Run button which opens a matplotlib figure to display the plot of the diffraction pattern and of the map image under construction. During this processing, one can select a scatering range to highlight the regions of interest.
Further analysis can be performed on the resulting dataset using the PyMca roitool where the 1d dataset has to be selected as last dimension. The result file aims at NeXus compliance.
This tool can be used for tomography experiments if one considers the slow scan direction as the rotation.
The user interface can be disabled to allow scripting interface and providing a JSON configuration file (or all the options).
Usage:¶
diff_map [options] imagefiles*
- positional arguments:
FILE List of files to integrate. Mandatory without GUI
- optional arguments:
- -h, --help
show this help message and exit
- -V, --version
show program’s version number and exit
- -o FILE, --output FILE
HDF5 File where processed map will be saved. Mandatory without GUI
- -v, --verbose
switch to verbose/debug mode, default: quiet
- -P FILE, --prefix FILE
Prefix or common base for all files
- -e EXTENSION, --extension EXTENSION
Process all files with this extension
- -t FAST, --fast FAST
number of points for the fast motion. Mandatory without GUI
- -r SLOW, --slow SLOW
number of points for slow motion. Mandatory without GUI
- -c NPT_RAD, --npt NPT_RAD
number of points in diffraction powder pattern. Mandatory without GUI
- -d FILE, --dark FILE
list of dark images to average and subtract (comma separated list)
- -f FILE, --flat FILE
list of flat images to average and divide (comma separated list)
- -m FILE, --mask FILE
file containing the mask, no mask by default
- -p FILE, --poni FILE
file containing the diffraction parameter (poni-file), Mandatory without GUI
- -O OFFSET, --offset OFFSET
do not process the first files
- -g, --gpu
process using OpenCL on GPU
- -S, --stats
show statistics at the end
- --gui
Use the Graphical User Interface
- --no-gui
Do not use the Graphical User Interface
- --config CONFIG
provide a JSON configuration file
Bugs:¶
If the number of files is too large, use double quotes “*.edf”
There is a known bug on Debian7 where importing a large number of file can take much longer than the integration itself: consider passing files in the command line